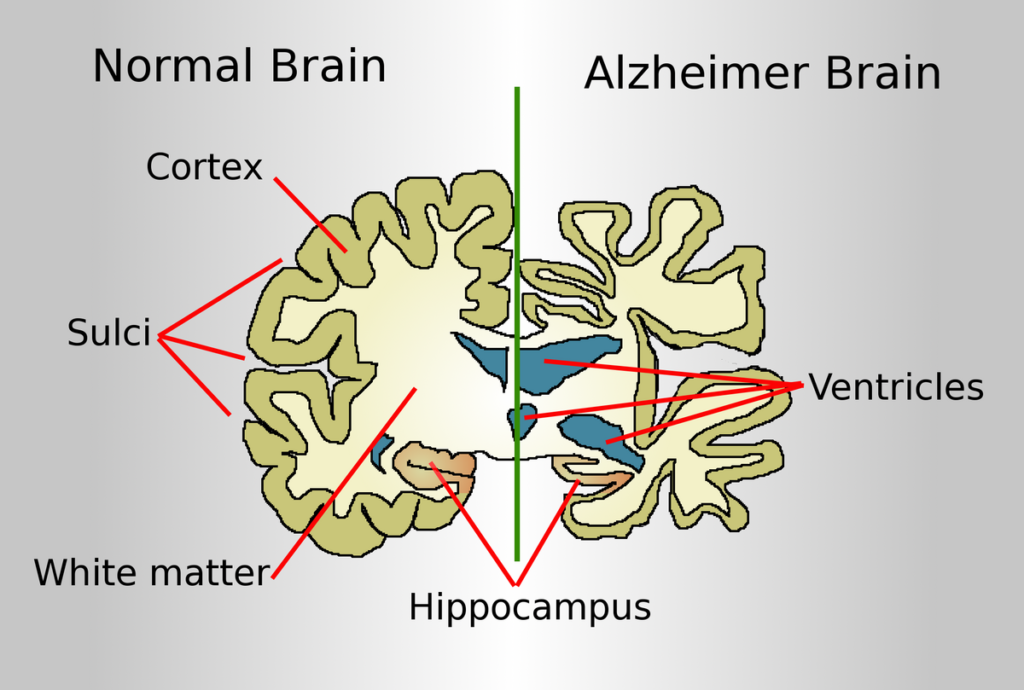
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive brain disorder that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. It is the most common cause of dementia, impacting millions of people worldwide. As the disease progresses, it severely affects daily life, making even simple tasks difficult. Despite years of research, there is still no cure for Alzheimer’s. However, recent advancements in treatment and ongoing studies offer hope for slowing the disease and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Why Does Alzheimer’s Occur?
Alzheimer’s disease develops due to complex changes in the brain, primarily caused by abnormal protein buildup. The two main proteins linked to Alzheimer’s are:
- Beta-amyloid plaques – Clumps of protein that form between nerve cells, disrupting communication and leading to cell death.
- Tau tangles – Twisted strands of another protein that accumulate inside brain cells, causing dysfunction and degeneration.
Other factors contributing to Alzheimer’s include:
- Genetics – People with a family history of Alzheimer’s have a higher risk.
- Aging – The likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s increases with age, especially after 65.
- Lifestyle and environmental factors – Poor diet, lack of exercise, high stress levels, and chronic conditions like diabetes and heart disease can increase the risk.
What Are the Symptoms of Alzheimer’s?
The symptoms of Alzheimer’s often develop slowly and worsen over time. Common signs include:
- Memory loss – Forgetting recent events, names, and important details.
- Confusion – Difficulty understanding time, place, and familiar people.
- Difficulty with tasks – Struggling to manage finances, cook, or complete daily routines.
- Personality changes – Mood swings, aggression, or withdrawal from social activities.
- Language problems – Trouble finding the right words or following conversations.
Early detection is crucial, as timely interventions can help manage symptoms and slow progression.


Current Treatments for Alzheimer’s
While there is no cure, several treatments help manage symptoms and improve daily function.
1. Medications for Symptom Management
- Cholinesterase inhibitors (Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine) – These drugs help improve memory and thinking by increasing levels of neurotransmitters in the brain.
- Memantine – Helps regulate glutamate, a chemical that plays a key role in learning and memory.
2. New FDA-Approved Drugs
Recent breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s treatment focus on slowing disease progression:
- Aducanumab (Aduhelm) – The first drug approved to target and reduce beta-amyloid plaques, slowing cognitive decline in early-stage Alzheimer’s.
- Lecanemab (Leqembi) – Another drug that reduces amyloid buildup and has shown promise in delaying symptoms.
3. Experimental Treatments and Future Research
- Immunotherapy – Scientists are developing vaccines and antibody treatments to stop protein buildup in the brain.
- Stem Cell Therapy – Research is exploring how stem cells might regenerate damaged brain cells.
- Gene Therapy – Scientists are investigating genetic modifications to prevent Alzheimer’s in at-risk individuals.
Can Alzheimer’s Be Prevented?
Although there is no guaranteed way to prevent Alzheimer’s, certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk:
1. Brain-Healthy Diet
- The Mediterranean diet (rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and healthy fats) supports brain health.
- Foods rich in antioxidants (like berries and nuts) help protect brain cells.
2. Regular Exercise
- Physical activity improves blood flow to the brain and reduces the risk of cognitive decline.
- Even simple activities like walking, yoga, or swimming can help.
3. Mental Stimulation
- Engaging in puzzles, reading, learning new skills, or socializing keeps the brain active.
- Lifelong learning reduces the risk of developing dementia.
4. Quality Sleep
- Poor sleep has been linked to an increased risk of Alzheimer’s.
- Establishing good sleep habits can help prevent memory decline.
5. Stress Management
- Chronic stress can damage brain cells.
- Meditation, deep breathing, and relaxation techniques can help maintain brain health.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Research
Scientists are continuously working to discover new treatments and, potentially, a cure for Alzheimer’s. Areas of focus include:
- Personalized medicine – Treatments tailored to individuals based on genetics and biomarkers.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnosis – Using AI to detect Alzheimer’s earlier and more accurately.
- Drug development – Creating new medications that target different aspects of the disease.
Conclusion
While Alzheimer’s remains an incurable disease, recent advancements in treatment offer hope for slowing its progression and improving quality of life. Medications, lifestyle changes, and ongoing research are paving the way for better management and, one day, a possible cure. In the meantime, early diagnosis, proactive brain care, and supportive therapies remain the best ways to combat this devastating condition.